
Curious children are a series suitable for children in all ages. If you have a question, you want an expert to answer, please send it to the Curiouskidsus@theconversation.com.
Where is black on the color spectrum? -UTSAV, 17 years old, Mahara Shilastra, India Navi Mumbai
People like Roygbiv color rainbow: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, blue and violet. Human eyes regard the visible light as this color.
However, you may notice that some colors you can perceive are not part of the classic rainbow. For example, where is black?
I am an associate professor in color science, which combines physics and perception in this field. Color scientists are interested in learning more information about human vision, and use these knowledge to make color systems (such as in cameras, screens, or lighting systems) to better work.
To understand the position of black on the color spectrum, first consider what light is.
Dispendicular radiation alone
Light is called electromagnetic radiation. It consists of energy particle flow called photon.
Each photon has its own energy level. You can use two features to describe photons. Its frequency is the speed (or oscillation) it is vibrated (or oscillated) when traveling. Its wavelength is the distance between these oscillations in the space.
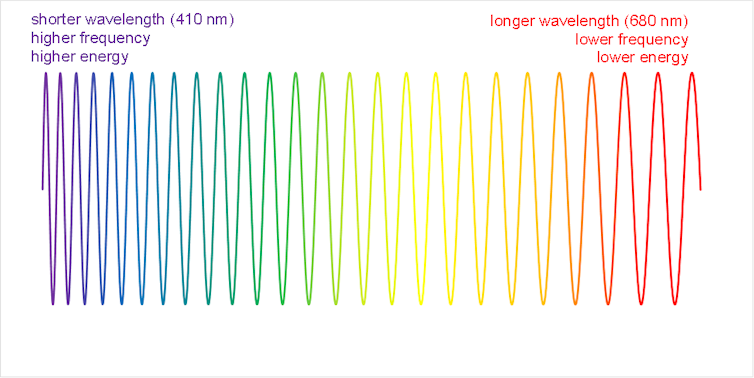
When a photon with a wavelength in a range of about 400–700 nanometer enters your eyes, your brain regards it as light. Scientists say these photons are visible to radiation. You can treat photons with different wavelengths as different colors.
The photons outside the wavelength are invisible to human eyes. The short wavelength energy includes ultraviolet rays, X -rays and gamma rays, and long wavelength energy includes infrared and radio waves.
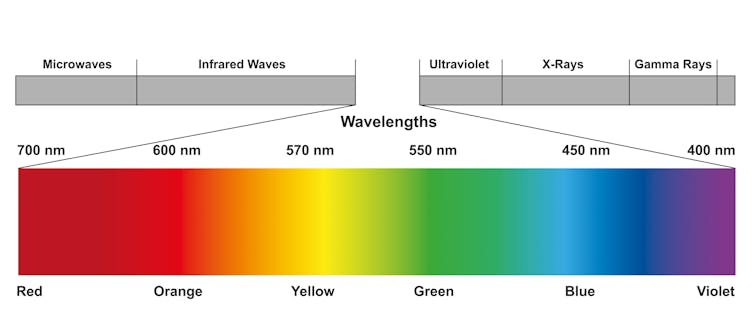
Shadow and strength
In different visible wavelengths, color perception is also affected by the number of photons (the power of the physicist). More photons mean more powerful light and look brighter. The very vivid color is mainly composed of photons with similar wavelengths. For example, pure red may be composed of photons, and they share the same wavelength near 620 nanometers.
Photon streams with a larger wavelength range will be displayed as lighter and less saturated. White light, such as natural sunlight, consisting of wavelengths of photon, is quite uniformly spread in a wide range of visible spectrals. The LED and other electric lamp sources are not so uniform in the entire spectrum, but they still look white or considerable, meaning no color.
The combination of the wavelength mixture is displayed as a new color. The human vision system is interpreted as pure red and pure green lights, combined with yellow. Add pure blue, the mixture of this radiation looks white. Scientists and engineers use this quality in the display device. By mixed red, green, and blue main colors, they can create a lot of perceived colors.
Black color spectrum
Although there is no black in the rainbow, photons in the electromagnetic spectrum can be regarded as black anywhere. Or in some cases, you can't see them at all!
If the radiation power in the spectrum is low, the radiation in the spectrum may be black-more specifically, the power is lower than the surrounding environment.
In addition, in our eyes, the radiation outside the wavelength is black in our eyes. For example, infrared radiation looks black because it is invisible to humans.
Perception is subjective
Our eyes detected the wavelength and strength of light, but our brain explained it. Therefore, color perception always depends on the context.
People are good at adapting to the extensive light from the sun to starlight. Therefore, our views on colors and brightness depends on the surroundings and what we have seen recently. If you turn from outdoor sunlight to the Dark Theater, at the beginning, you may see the entire environment as black, and it may even be difficult to find your own way.
However, your visual system immediately began to adapt to low light. Soon, visual details began to appear. The black now appears now has different levels of brightness and color.

Consider the illusion of a light rectangle next to the dark rectangle. Each rectangle contains a circle. The circular shape seems to be different, but it is actually the same. In the background of light, the circle is dark enough to look black. Surrounded by the black background, it is clear that the circle is only dark gray. Even if you know that the circle is the same, it is difficult to believe, because the effect of the surrounding background is so powerful.

You may ask yourself, how dark the color must be black? Another way to ask questions is, how low the power of physical light must be black?
For visual answers, check the gradient from dark gray to black. Where is the border or threshold, do you call it black? What should I do if you tone or view the screen in a brighter or darker environment? It may be the darkest of the "it depends on".
Color perception is a fascinating topic. We continue to reveal the details of how the human visual system operates for scientists. At the same time, we also apply our knowledge to many other useful things, including dyes, cameras, printers, LED lighting systems and AR/ AR/ VR display.
Hello, a curious child! Do you want experts to answer questions? Adults are required to send your question to Curiouskidsus@theconversation.com. Please tell us your name, age and the city where you live.
And, because curiosity has no age restriction-adults, let us know what you are thinking. We will not be able to answer every question, but we will do our best.